Photosynthesis Worksheets
About Our Photosynthesis Worksheets
Our Photosynthesis worksheets offer an engaging and comprehensive way for students to learn about one of the most fundamental processes in biology. As a key subtopic under Biology and Plants, these worksheets provide a deep dive into how plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Each worksheet set includes a detailed reading passage accompanied by a visually engaging and relevant picture, followed by various question formats to reinforce understanding and encourage critical thinking.
Each worksheet set includes:
- Multiple Choice Questions: These questions assess students' comprehension of the reading passage by offering a selection of answers, reinforcing key facts and concepts about photosynthesis.
- Short Answer Questions: In this section, students write their own answers based on the reading passage. This format encourages them to articulate their understanding in their own words, deepening their grasp of the material.
- Open-Ended Questions: These questions prompt students to share personal input, opinions, or reflections related to the reading material. This format fosters a deeper connection with the topic, encouraging students to relate photosynthesis to their own experiences and broader environmental understanding.
Each worksheet also includes an answer key, making it easy for teachers and parents to review and assess students' work. All worksheets are available as PDF files, which can be easily viewed electronically, downloaded, and printed for use in classrooms or homeschool settings.
Photosynthesis: The Powerhouse of Plant Life
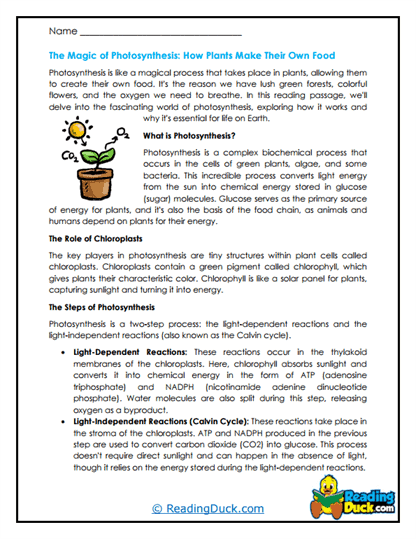
Photosynthesis is a critical process that sustains life on Earth. It is the means by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose, a type of sugar. This process not only fuels the growth and development of plants but also produces oxygen, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms. When introducing students to photosynthesis, it’s important to highlight its significance not only for plants but for all life on Earth.
What Is Photosynthesis?
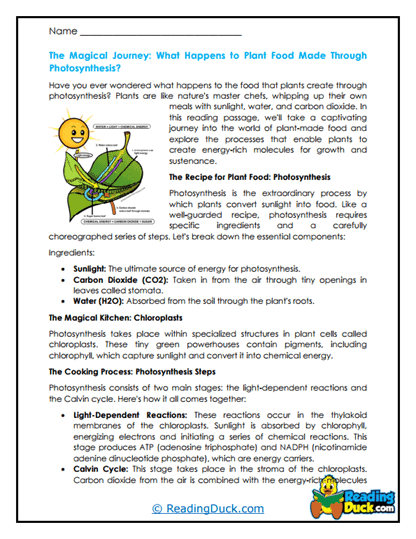
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process that occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which captures sunlight. The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
- The Light-Dependent Reactions:
- Location: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts.
- Process:
- Sunlight Absorption: Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which excites electrons and triggers a chain of reactions.
- Water Splitting: The absorbed energy is used to split water molecules (H₂O) into oxygen (O₂), protons, and electrons. The oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- Energy Conversion: The energy from the excited electrons is used to convert ADP and NADP⁺ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH, which are then used in the next stage of photosynthesis.
- The Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions):
- Location: These reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
- Process:
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere is fixed into an organic molecule.
- Sugar Formation: The ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions provide the energy to convert the fixed carbon into glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), which the plant can use as a source of energy or store for later use.
- Regeneration: The cycle regenerates the starting material, allowing the process to continue as long as there is light and carbon dioxide.
Why Is Photosynthesis Important?
Photosynthesis is not just a process that benefits plants; it is the foundation of life on Earth. Here’s why photosynthesis is so vital:
- Energy Production:
- For Plants: Photosynthesis is how plants produce the energy they need to grow, develop, and reproduce. The glucose produced can be used immediately for energy or stored as starch for later use.
- For Animals: Animals, including humans, rely on the energy stored in plants for their own survival. When animals eat plants, they consume the energy that plants have stored through photosynthesis.
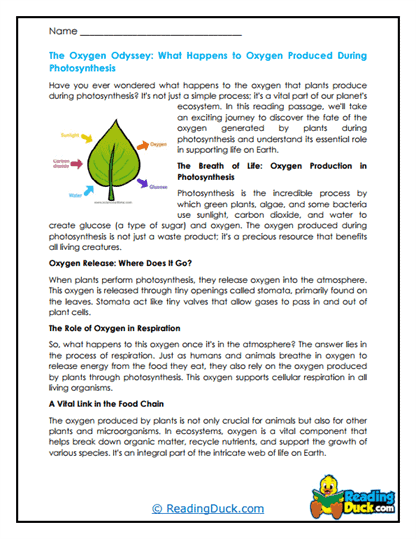
- Oxygen Production:
- Atmospheric Balance: Photosynthesis is responsible for producing the oxygen we breathe. By converting carbon dioxide into oxygen, plants help maintain the balance of gases in the atmosphere, which is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms.
- Supporting Life: The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released into the atmosphere, supporting the respiratory needs of nearly all living organisms on Earth.
- Carbon Dioxide Regulation:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gases: Photosynthesis plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate by removing carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, from the atmosphere. This helps mitigate the effects of global warming and climate change.
- Supporting Ecosystems:
- Food Chains: Photosynthesis is at the base of most food chains. Plants produce the energy that is passed on to herbivores and then to carnivores, supporting a diverse range of life forms in various ecosystems.
- Habitat Formation: Plants also provide habitats and food for countless organisms, from insects to large mammals, creating and sustaining ecosystems around the world.
How Do Plants Optimize Photosynthesis?
Plants have developed various adaptations to optimize photosynthesis, depending on their environment:
- Leaf Structure:
- Broad Leaves: Many plants, especially those in sunny environments, have broad leaves that increase the surface area for light absorption.
- Stomata: Leaves have tiny openings called stomata that regulate gas exchange. They open to allow carbon dioxide in and oxygen out, while also controlling water loss through transpiration.
- Chloroplast Arrangement:
- Maximizing Light Capture: Chloroplasts are often positioned in the cells to capture the maximum amount of light. In low-light conditions, some plants can move their chloroplasts within their cells to optimize light absorption.
- C4 and CAM Pathways:
- C4 Photosynthesis: Some plants, like corn and sugarcane, use a modified version of photosynthesis called C4 photosynthesis. This adaptation allows them to thrive in hot, dry environments by efficiently capturing carbon dioxide and minimizing water loss.
- CAM Photosynthesis: CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis is an adaptation found in desert plants, such as cacti, that allows them to photosynthesize while minimizing water loss. These plants open their stomata at night to take in carbon dioxide and store it for use during the day.
Using These Worksheets Effectively
Teachers and parents can use these Photosynthesis worksheets in a variety of creative and effective ways to enhance student learning:
- Photosynthesis Lab Experiment: Have students conduct a simple experiment where they observe photosynthesis in action, such as by placing a leaf in water and exposing it to sunlight to see oxygen bubbles form. This hands-on activity reinforces the concepts learned in the worksheets and makes the process of photosynthesis more tangible.
- Create a Photosynthesis Model: Encourage students to create a 3D model of a chloroplast or the entire photosynthesis process. This project helps students visualize the components and stages of photosynthesis, deepening their understanding through creative expression.
- Photosynthesis and Global Warming Discussion: Use the worksheets as a starting point for a discussion on how photosynthesis relates to global warming. Students can explore the role of plants in reducing carbon dioxide levels and discuss the importance of preserving forests and other green spaces.
- Illustrated Photosynthesis Diary: Have students keep an illustrated diary over a week, tracking how different factors (such as light intensity, water, and temperature) affect a plant’s ability to photosynthesize. This activity encourages observation and critical thinking, allowing students to connect the theory of photosynthesis to real-world conditions.
The Critical Role of Photosynthesis in the Real World
Photosynthesis is more than just a biological process; it is the foundation of life on Earth. It sustains plant life, which in turn supports all other forms of life by providing food and oxygen. Moreover, photosynthesis plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by reducing carbon dioxide levels, thereby helping to mitigate global warming. Understanding photosynthesis gives students insight into how energy flows through ecosystems, the importance of plants in our world, and the interconnectedness of all living things. In the broader context, this knowledge emphasizes the need to protect our natural environment, ensuring that photosynthesis—and the life it supports—can continue for future generations.