Alphabet Worksheets
About Our Alphabet Worksheets
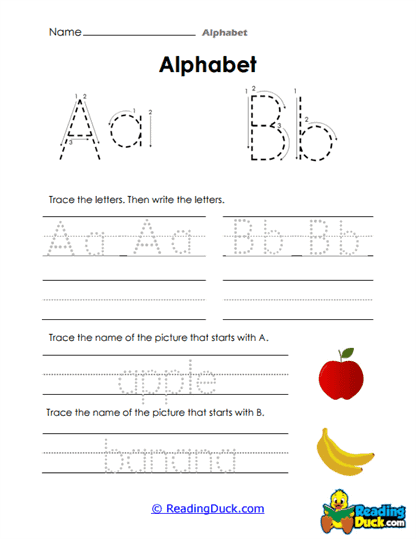
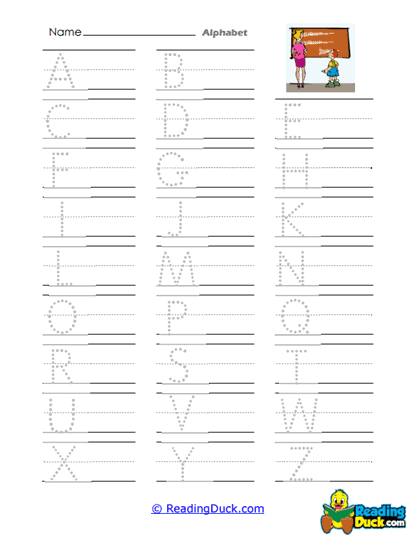
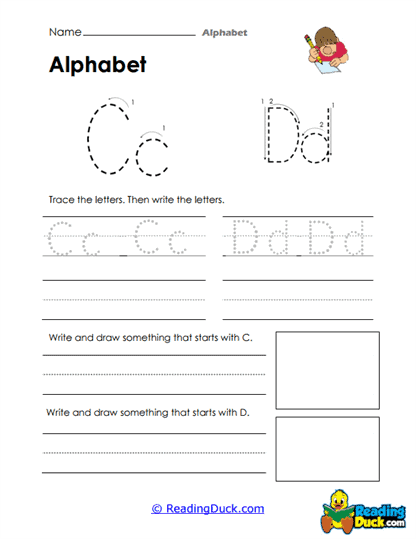
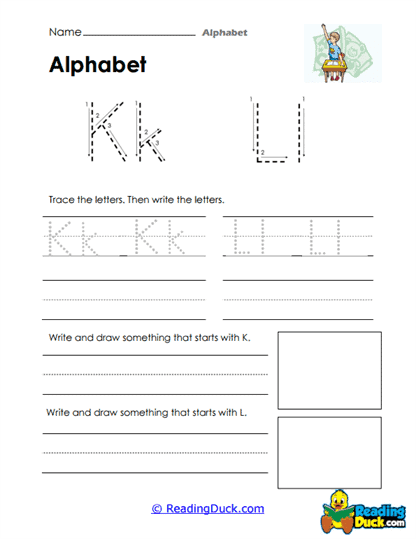
Our collection of Alphabet Worksheets is an essential resource for young learners as they begin to build foundational language skills. This collection falls under the Language category within the Skills section, focusing on the essential task of helping children recognize, read, and write every letter of the alphabet. These worksheets guide students step by step through letter formation and identification, providing them with the tools they need to develop early literacy skills. By focusing on letter tracing and recognition, along with exercises that connect beginning sounds to words and illustrations, these worksheets promote a multi-sensory approach to learning the alphabet.
These worksheets focus on helping young learners recognize, read, and write all the letters of the alphabet. They contain a variety of exercises, including tracing letters, tracing words that begin with certain sounds, and associating these words with their corresponding illustrations. The worksheets are presented in a convenient PDF format, making them simple to view, download, and print. Additionally, each worksheet includes a downloadable answer key, allowing for easy self-assessment and guidance.
Understanding the Alphabet: The Foundation of Language
The alphabet is the building block of language. It is a set of written symbols, each representing a sound, which can be combined to form words. The alphabet provides a standardized system for reading and writing, allowing us to translate spoken sounds into visual symbols that can be shared and understood universally.
The Structure of the Alphabet:
Letters: The alphabet consists of individual letters, each representing a specific sound or group of sounds. In the English language, there are 26 letters, divided into two categories:
-
- Vowels: A, E, I, O, U (and sometimes Y). These are the letters that form the core of syllables and play a key role in word construction.
- Consonants: The remaining 21 letters, which provide structure and form to words.
Letter Recognition: The ability to recognize each letter, both in uppercase and lowercase, is the first step in learning to read. It allows children to identify individual letters within words and understand how they come together to form sounds and meaning.
Phonetic Awareness:
- Sound-Letter Correspondence: Each letter of the alphabet corresponds to a sound (or sometimes multiple sounds). Understanding this relationship between letters and sounds is crucial for reading development, as it allows children to decode words and understand their meanings.
Writing the Alphabet:
- Letter Formation: Learning how to correctly form each letter by tracing its shape is a key motor skill that reinforces letter recognition. Tracing helps children develop fine motor control while also solidifying their understanding of each letter’s unique form.
By mastering the alphabet, students gain the fundamental skills necessary for future reading, writing, and communication. The alphabet acts as a gateway to literacy, enabling children to break down words into manageable parts and build the confidence to tackle more complex language tasks.
Common Challenges and Strategies for Learning the Alphabet
Learning the alphabet, while foundational, can present certain challenges for young learners. Some students may struggle with recognizing letters, differentiating between similar-looking letters, or remembering letter-sound relationships. Educators can help students overcome these challenges by incorporating strategies that make alphabet learning more accessible and engaging.
Common Challenges:
- Letter Confusion: Students may confuse letters that look or sound alike, such as “b” and “d” or “p” and “q.” This can lead to difficulty in correctly identifying and writing letters.
- Phonetic Inconsistencies: English has many phonetic irregularities, making it hard for students to consistently match letters with their sounds. For example, the letter “c” can sound like a “k” (cat) or an “s” (ceiling).
- Memory Retention: Remembering all 26 letters and their corresponding sounds can be overwhelming for young students, especially when they are first exposed to the alphabet.
Effective Strategies:
- Visual Aids and Mnemonics: Visual aids such as alphabet charts, flashcards, or illustrated letter books can help students remember letters more easily by associating them with familiar images. For instance, pairing the letter “A” with a picture of an apple reinforces both the shape and sound of the letter.
- Kinesthetic Learning: Incorporating hands-on activities such as tracing letters with fingers, forming letters with clay, or drawing letters in sand can make learning more tactile and engaging. These methods help strengthen motor memory and reinforce letter shapes.
- Repetition and Practice: Regular practice is key to solidifying letter recognition. Incorporating short, frequent practice sessions allows students to reinforce what they’ve learned and gradually build confidence. Educators can also create songs or rhymes to help students remember the order of the letters in the alphabet.
- Differentiation: Some students may benefit from additional support, such as focusing on a few letters at a time or grouping similar-looking letters together for comparison. Breaking the alphabet into smaller sections helps prevent students from becoming overwhelmed.
These strategies not only help students learn the alphabet more effectively but also create an enjoyable learning experience that encourages active participation and confidence in their growing literacy skills.
How Alphabet Mastery Enhances Literacy
The alphabet is the cornerstone of literacy development. Mastery of the alphabet equips students with the skills they need to become proficient readers, writers, and communicators. By recognizing and understanding the letters of the alphabet, students are prepared to engage with more advanced language skills, such as phonics, spelling, and sentence formation.
Early Reading Skills:
Learning the alphabet lays the groundwork for decoding words, which is an essential step in reading development. When students understand how letters combine to form sounds, they are able to decode unfamiliar words by breaking them down into individual letter sounds. This knowledge supports reading fluency, as students can read with greater speed and accuracy once they recognize letter-sound patterns.
Writing and Spelling:
Mastering the alphabet also enhances writing skills. As students learn to form letters correctly, they gain the ability to spell simple words and begin constructing sentences. Writing the alphabet repeatedly helps children develop fine motor skills, which are necessary for clear and legible handwriting.
Speaking and Listening:
The alphabet is closely tied to phonemic awareness, which is the ability to hear and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words. By learning the sounds that each letter represents, students become better listeners and speakers, as they can articulate sounds more clearly and understand spoken language with greater precision.
Fun and Engaging Activities to Reinforce Alphabet Learning
In addition to using the Alphabet Worksheets, educators can introduce various activities to make learning the alphabet both fun and effective. These activities are suitable for students in pre-kindergarten through first grade, providing additional practice in school or homeschool environments.
Alphabet Games:
- Alphabet Bingo: Create bingo cards with different letters of the alphabet. As the teacher calls out letters, students mark them off on their cards. This game encourages letter recognition in a fun and interactive way.
- Letter Matching: Provide students with a set of uppercase and lowercase letter cards. Have them match each uppercase letter with its corresponding lowercase form. This helps reinforce the connection between different forms of the same letter.
Hands-On Activities:
- Letter Hunt: Hide letter cards around the classroom or home. Students can search for the letters and name them as they find them. This active game promotes letter recognition and recall.
- Alphabet Puzzles: Use puzzles where students match letters with pictures of objects that begin with those letters. This visual and hands-on activity helps students connect letters with beginning sounds, making phonics practice more engaging.
Creative Writing Prompts:
Encourage students to write words or simple sentences using the letters they’ve learned. For example, have them write about an animal whose name starts with a specific letter, such as “A is for Alligator.” This activity promotes creativity while reinforcing letter recognition and sound association.
The Practical Importance of Alphabet Knowledge
Mastering the alphabet is one of the most critical skills that students acquire during their early years of education. It forms the basis of all future literacy development, enabling students to progress toward more advanced language tasks like reading complex texts, writing stories, and communicating effectively.
In real life, knowing the alphabet allows students to navigate everyday tasks that require literacy, from reading signs and labels to filling out forms and engaging in written communication. The ability to understand and use the alphabet fluently provides students with the tools they need to succeed academically and socially, making it an indispensable part of their education and future development.
In summary, the Alphabet Worksheets provide an excellent foundation for students to master the alphabet, enhancing their ability to read, write, and communicate with confidence. The worksheets, combined with engaging activities and strategies, ensure that students build a strong, lasting understanding of this fundamental language skill.