Plurals Worksheets
About Our Plural Worksheets
This collection of Plurals Worksheets, categorized under the Language section within the Skills category, serves as an essential tool for students learning how to correctly form plural nouns. Mastery of pluralization is a foundational language skill that impacts both writing and reading comprehension. Understanding how to change singular nouns into their plural forms strengthens a student’s grammar abilities, helping them become more precise and articulate in their communication.
The worksheets in this collection are designed to be clear and accessible, available in PDF format to allow for easy viewing, downloading, and printing. Each worksheet is paired with a downloadable answer key to support teachers and parents in guiding students through the content. Whether used in the classroom or a homeschool setting, these worksheets provide ample opportunities for students to practice plural formation and improve their overall language proficiency.
Exploring Plurals: Understanding Singular and Plural Nouns
Plurals refer to the grammatical form that indicates more than one of something. In English, forming plurals often involves adding an "s" or "es" to a singular noun, but there are several rules and exceptions that students must learn to master the concept fully. The ability to recognize and form plurals correctly is an essential part of a student’s early grammar education and builds the foundation for more complex language skills later on.
What Are Plurals?
Plurals are the forms of nouns used to indicate more than one person, animal, object, or idea. While the most common way to form a plural is by adding "s" to the end of a singular noun, English has a range of pluralization rules depending on the spelling and pronunciation of the word.
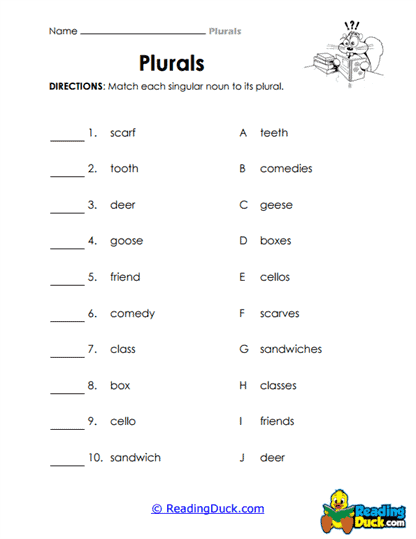
- Regular Plurals: The most straightforward way to form a plural is by adding "s" to the end of the word. For example, "cat" becomes "cats," and "book" becomes "books."
- Plurals with “es”: Nouns that end in "s," "x," "ch," "sh," or "z" typically take "es" instead of just "s." For example, "box" becomes "boxes," "wish" becomes "wishes," and "church" becomes "churches."
- Plurals with “ies”: For nouns that end in a consonant followed by a "y," the "y" is usually dropped and replaced with "ies." For instance, "baby" becomes "babies," and "story" becomes "stories."
Irregular Plurals
Some nouns do not follow the regular pluralization rules and require special attention. These irregular plurals often pose more challenges for students since they must memorize each unique form.
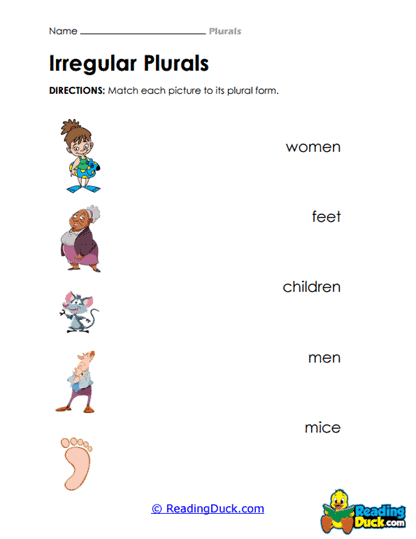
- Nouns that change form: Some singular nouns change completely in their plural form. For example, "man" becomes "men," and "child" becomes "children."
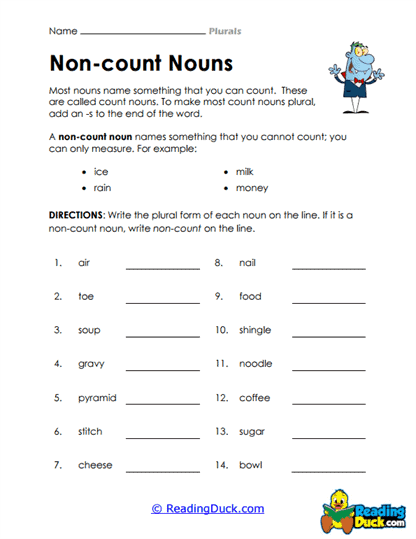
- Unchanging nouns: Certain nouns do not change in their plural form. For example, "sheep" remains "sheep," and "deer" remains "deer," regardless of how many there are.
- Nouns with foreign roots: Words that come from Latin, Greek, or other languages often have irregular plural forms. For instance, "criterion" becomes "criteria," and "cactus" becomes "cacti."
Special Plural Forms
There are also some special cases where pluralization may require additional rules:
- Compound nouns: When pluralizing compound nouns (nouns made up of two or more words), the main noun typically takes the plural form. For example, "mother-in-law" becomes "mothers-in-law," and "passerby" becomes "passersby."
- Plural of letters, numbers, and symbols: To avoid confusion, plurals of letters, numbers, and symbols are formed by adding an apostrophe followed by an "s" (e.g., "Mind your p's and q's" or "The 1970's").
By learning these pluralization rules, students can avoid common grammar mistakes and become more accurate in their writing and speaking.
Overcoming Common Challenges When Learning Plurals
Learning how to correctly form plurals can be tricky for young students, especially when irregular plural forms and exceptions come into play. There are several challenges students might face when beginning to learn pluralization rules, but educators can provide strategies to help them overcome these difficulties.
Challenges Students Face
- Memorizing Irregular Plurals: One of the biggest challenges students encounter is remembering irregular plural forms that don’t follow the basic "add an s" rule. For instance, words like "mouse" (which becomes "mice") or "foot" (which becomes "feet") may confuse students who are used to regular pluralization patterns.
- Confusing Similar-Looking Words: Certain singular and plural forms look similar, which can lead to mistakes in usage. For example, "deer" can be both singular and plural, which may cause confusion in writing and speaking.
- Dealing with Special Cases: Compound nouns and nouns with foreign roots can present a special challenge. For instance, students may not intuitively understand why "mother-in-law" becomes "mothers-in-law" instead of "mother-in-laws."
Strategies for Mastery
Educators can help students grasp the concept of plurals through various methods and practice techniques. Here are a few strategies that can improve students’ retention and understanding:
- Visual Aids and Word Lists: Providing charts or flashcards that categorize regular and irregular plural nouns can make it easier for students to learn the rules visually. Grouping similar words together (e.g., all "es" plurals or all irregular forms) can reinforce the patterns in their minds.
- Frequent Practice: Regular exposure and practice are key to mastering plural forms. Educators can encourage students to create sentences or short stories using a mix of singular and plural nouns, helping to solidify their understanding of how to switch between forms.
- Mnemonic Devices: Using memory aids can help students recall difficult plurals. For instance, a phrase like "A man and a mouse, two men and some mice" can help students remember the irregular plurals of these nouns.
- Reinforce Context: Teaching students to recognize plurals in context can help them understand their function in sentences. Reading aloud and identifying plural nouns in books or classroom materials reinforces how pluralization is used in everyday language.
By addressing these challenges and applying practical strategies, students can confidently tackle pluralization and avoid common errors.
How Learning Plurals Boosts Literacy Skills
Mastering pluralization plays a crucial role in enhancing students' overall literacy. Plurals affect not only their grammatical accuracy but also their reading, writing, and speaking fluency. Understanding how to use plurals correctly enables students to communicate more effectively and comprehend texts at a higher level.
Enhancing Reading Skills
Recognizing and understanding plural nouns in reading materials improves students’ reading comprehension. When students know the difference between singular and plural forms, they can better interpret the meaning of sentences and follow the structure of a text more accurately.
- Example: In a sentence like "The cats were chasing the mice," knowing that "cats" and "mice" are plural helps students understand that there are multiple animals involved in the action.
Improving Writing Proficiency
Correct pluralization is essential for clear and grammatically sound writing. When students know how to pluralize nouns accurately, their writing becomes more precise and easier to follow, allowing them to express ideas more clearly.
- Example: A student who correctly writes "The children played with the toys" demonstrates an understanding of plural forms, enhancing the quality and readability of their work.
Strengthening Speaking and Listening Skills
Using plurals correctly in speech is a sign of fluency. When students can form and use plural nouns appropriately in conversation, they communicate more effectively and with greater accuracy. Additionally, being able to distinguish between singular and plural forms in listening activities aids comprehension.
- Example: In a discussion about animals, using plural forms like "wolves" instead of "wolf" helps students convey their ideas accurately and participate meaningfully in conversation.
Engaging Activities to Reinforce Plural Learning
To help students master the concept of plurals, educators can incorporate a variety of interactive and enjoyable activities into their lessons. These activities encourage students to apply what they’ve learned in a fun, engaging way and are suitable for different grade levels.
Activities for Grades 1-3
- Plural Noun Bingo: Create bingo cards featuring both singular and plural nouns. As the teacher calls out a singular noun, students must find the correct plural form on their cards. This game helps younger students reinforce their understanding of basic pluralization rules in a playful setting.
Activities for Grades 4-6
- Plural Noun Word Search: Create word searches that contain both singular and plural nouns. Students are tasked with finding and circling the plurals, then writing sentences using those words. This activity helps with plural recognition while encouraging sentence construction.
Activities for Grades 7-9
- Plural Noun Story Writing: Have students write short stories that must include a set number of plural nouns. For instance, they could be required to use at least 10 irregular plural nouns. This creative exercise reinforces plural usage while fostering writing skills.
By incorporating these types of activities, educators make learning about plurals more interactive and memorable.
The Importance of Learning Plurals for Real-World Communication
Learning how to form and use plurals correctly is a fundamental language skill that students will carry with them throughout their academic and personal lives. In real-world communication, understanding pluralization is essential for writing accurate reports, engaging in conversations, and interpreting information. Whether students are reading a novel, composing an essay, or participating in a group discussion, proper plural usage helps them communicate ideas clearly and effectively.
By mastering pluralization, students enhance their language skills and lay the groundwork for more advanced grammar topics, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of language in both academic and everyday contexts.