Weather Worksheets
About Our Weather Worksheets
Our collection of Weather worksheets provides a comprehensive and engaging exploration of the various elements that define and influence weather patterns. As part of the broader Earth Science curriculum, these worksheets are designed to help students understand the fundamental concepts of weather, from the basic components like temperature and humidity to more complex phenomena like storms and climate patterns.
Each worksheet set includes:
- Multiple Choice Questions: These questions assess students' understanding of the key concepts presented in the reading passages, reinforcing their knowledge and ensuring they grasp the essentials of weather science.
- Short Answer Questions: These prompts encourage students to articulate their understanding in their own words, promoting deeper comprehension and the ability to apply their knowledge.
- Open-Ended Questions: These questions invite students to engage critically and creatively with the material, asking them to express personal insights, opinions, or connections to the weather concepts they've learned.
An answer key accompanies each worksheet, making it easy for teachers and parents to check students' progress. All worksheets are available in PDF format, which can be easily accessed electronically, downloaded, and printed for use in the classroom or at home.
Exploring Weather: Understanding the Dynamics of Earth’s Atmosphere
1. The Basics of Weather
- Temperature and Air Pressure:
- Temperature is one of the most fundamental elements of weather. It measures the warmth or coldness of the atmosphere, influencing other weather conditions. Air pressure, on the other hand, is the weight of the air above us. It plays a crucial role in determining weather patterns, with high-pressure systems typically bringing fair weather and low-pressure systems often associated with storms.
- Humidity and Precipitation:
- Humidity refers to the amount of moisture in the air. It affects how comfortable we feel and influences the formation of clouds and precipitation. When the air becomes saturated with moisture, it leads to precipitation, which can take the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail. Understanding these processes helps students grasp how weather is formed and why it varies in different regions and seasons.
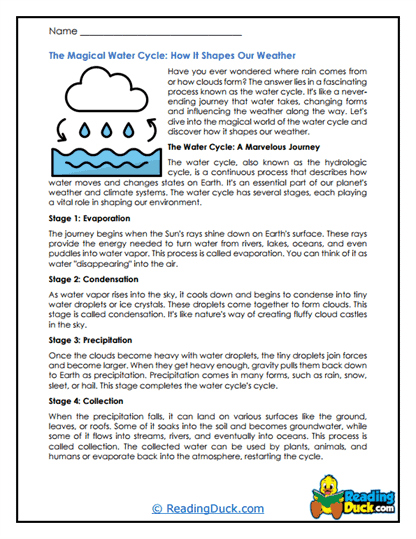
2. The Water Cycle and Weather Patterns
- Evaporation, Condensation, and Precipitation:
- The water cycle is a continuous process that drives much of the Earth's weather. Water evaporates from the Earth's surface, rises into the atmosphere, and condenses into clouds. When these clouds become heavy with moisture, precipitation occurs, returning water to the surface. This cycle is essential in maintaining the Earth's ecosystems and influencing weather patterns across the globe.
- Weather Systems and Fronts:
- Weather systems, including high and low-pressure systems, fronts, and air masses, are key players in determining weather patterns. Fronts, which are boundaries between different air masses, often bring significant changes in weather, such as the transition from warm to cold temperatures or the onset of precipitation. By understanding these systems, students can better predict and interpret daily weather changes.
3. Severe Weather Events
- Thunderstorms and Tornadoes:
- Thunderstorms are intense weather events characterized by lightning, thunder, heavy rain, and sometimes hail. They can also produce tornadoes, which are violent, rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. Understanding the formation and impact of these events helps students appreciate the power of nature and the importance of weather safety.
- Hurricanes and Blizzards:
- Hurricanes are large, powerful storms that form over warm ocean waters and can cause widespread destruction due to strong winds, heavy rains, and storm surges. Blizzards, on the other hand, are severe snowstorms with strong winds and low visibility, which can paralyze regions for days. Studying these phenomena enables students to understand the global and local impacts of extreme weather and the measures needed to prepare for such events.
4. The Difference Between Weather and Climate
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Atmospheric Conditions:
- While weather refers to the short-term conditions of the atmosphere at a specific time and place, climate describes the average weather conditions in a region over a long period, typically 30 years or more. This distinction helps students understand how daily weather patterns fit into broader climate trends, which are crucial for studying global changes such as global warming.
- Climate Zones and Their Characteristics:
- The Earth is divided into different climate zones, each with distinct weather patterns. These zones include tropical, temperate, and polar climates, among others. By studying these zones, students can learn how location and geography influence the climate and, consequently, the types of weather experienced in different parts of the world.
Activities to Supplement These Worksheets
To further enrich students' understanding of weather and make the learning experience more engaging, consider incorporating the following activities and projects:
1. Create a Weather Station
- Objective: Teach students how to observe and measure different weather elements.
- Activity: Students can construct simple weather instruments such as a thermometer (for temperature), a barometer (for air pressure), an anemometer (for wind speed), and a rain gauge (for precipitation). They can then use these tools to monitor and record daily weather conditions. This hands-on activity allows students to see how the various components of weather interact in real-time.
2. Weather Journals
- Objective: Develop observation skills and track weather changes over time.
- Activity: Encourage students to keep a daily weather journal where they note down the temperature, cloud cover, wind conditions, and any precipitation. They can also include drawings or photographs of the sky and reflections on how the weather influences their day. This activity helps students connect classroom knowledge to the world around them and recognize patterns in weather behavior.
3. Analyze Weather Maps
- Objective: Improve students’ ability to interpret weather data.
- Activity: Provide students with weather maps showing high and low-pressure systems, fronts, and precipitation. Ask them to analyze these maps to predict the weather for various regions and explain their reasoning. This activity sharpens critical thinking skills and deepens students' understanding of meteorology.
4. Severe Weather Safety Plans
- Objective: Teach students about preparedness and safety during extreme weather events.
- Activity: Have students research different types of severe weather and create safety plans for each one. These plans should include what to do before, during, and after events like tornadoes, hurricanes, and blizzards. This project not only reinforces their understanding of severe weather but also provides practical knowledge that could be vital in real-life situations.
5. Cloud Identification and Classification
- Objective: Help students learn about different cloud types and their implications for weather.
- Activity: Take students outside to observe and identify various cloud formations, such as cumulus, stratus, cirrus, and cumulonimbus clouds. Students can draw or photograph the clouds and classify them based on their characteristics and the weather they typically bring. This activity enhances observational skills and understanding of weather prediction.
6. Weather Forecast Project
- Objective: Introduce students to the basics of weather forecasting.
- Activity: Students can act as meteorologists by creating their own weather forecasts. They can use data from their weather journals, maps, and other resources to predict the weather for the coming days. Presenting these forecasts to the class allows students to practice communication skills and apply their weather knowledge in a real-world context.
7. The Impact of Weather on Daily Life
- Objective: Explore how weather influences various aspects of life.
- Activity: Assign students to research how weather affects agriculture, transportation, sports, or another area of interest. They can present their findings in a report or presentation, discussing how different weather conditions impact human activities and how societies adapt to these changes.
8. Interactive Weather Simulations
- Objective: Provide students with a dynamic way to explore weather concepts.
- Activity: Use online weather simulation tools that allow students to manipulate variables like temperature, humidity, and wind speed to see how these factors create different weather conditions. This interactive activity makes abstract concepts more tangible and engaging.
9. Debate on Climate Change and Weather Patterns
- Objective: Encourage students to think critically about the relationship between weather and climate change.
- Activity: Organize a debate or discussion on how climate change is affecting global weather patterns. Students can research and present different perspectives on topics such as the frequency of severe weather events, the impact on ecosystems, and strategies for mitigation and adaptation. This activity fosters critical thinking and informed discussion.
10. Weather Art Project
- Objective: Combine creativity with scientific learning.
- Activity: Students can create an art project that represents different types of weather, such as a painting of a stormy sky or a collage of various cloud types. This project allows students to express their understanding of weather through artistic mediums, reinforcing the science concepts they've learned in a creative and personal way.
By integrating these activities with the Weather worksheets, teachers and parents can provide a well-rounded educational experience that not only teaches students about weather but also inspires curiosity and a deeper appreciation for the natural world. These projects help solidify the knowledge gained from the worksheets and allow students to apply what they've learned in engaging and meaningful ways.